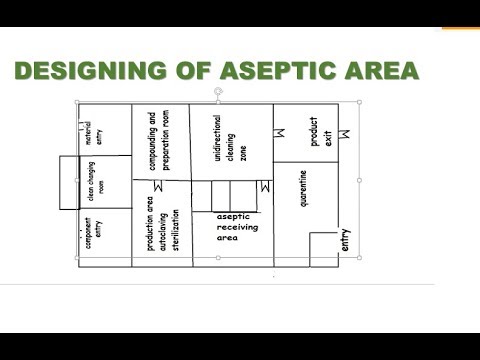
Designing of Aseptic Area
Aseptic area is the well-defined area where the production of sterile preparations should be carried out. Entry into this area is strictly through an airlock for personnel, equipment or materials. The operations of sterile preparation, filling and sterilization are performed under controlled conditions to minimize microbial and particulate contamination.
Significance of Aseptic Area- To provides a controlled environment so that the entrance of viable (microbial) and non-viable (particles) contaminants can be minimised.
- controlled environment prevents cross- contamination of Compounded Sterile Preparations (CSPs).
- controlling suspended particulate matter
- air flow pattern
- viable cell count
- electrostatic charges etc.
- air flow velocity control
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| Grade A | The local zone for high-risk operations, e.g., filling and making aseptic transfer |
| Grade B | Background area of Grade A processes (aseptic preparation and filling) |
| Grade C | Preparation of sterile solutions to be filtered |
| Grade D | Handling of components after washing |

The following factors are considered important when designing any aseptic area:
- All aseptic areas should avoid entry of unrelated personnel as far as possible.
- In all aseptic areas, all exposed surfaces, walls, roofs should be smooth, impervious and unbroken, free from any cracks to minimize the shedding or deposition of microbial cells.
- Doors should be carefully designed to avoid any passage for air, sliding doors are not allowed for aseptic areas. Swing doors should be open in the flow direction of the air or from positive air pressure side to negative (low) air pressure side.
- Pipes and ducts and other utilities should be installed in such a way that they do not create recesses, unsealed openings, and surfaces that are difficult to clean.
- Sinks and drains should be avoided as possible, and should be excluded from the area of Grade A and Grade B, because aseptic activities are carried out in these areas.
- Changing rooms should be designed as air locked, and physically separated to minimize microbial contamination.
- Air locked doors should not be open simultaneously, in double door entry opening of the door in such a way that when one door is open, the second door should be close and an warning alarm system should be there to warn in the condition of both the doors are open.
- False ceiling should be avoided to prevent contamination from the void space or any joint or cracks.
- A filtered air supply should be used to maintain a positive air pressure relative to surroundings. Positive air pressure means air flows from high pressure areas to negative (low) pressure area. The flow of air should be from inside the aseptic room to outside the room.
- HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) filters should be installed to filter the air, which is then supplied to the aseptic rooms. HEPA filters have the pore size of 0.2 microns, these filters retain the bacterial cells and release the air which is free from microorganisms and particulate matters.
- Any kind of conveyer belt should be avoided to pass from aseptic area, specially between Grade A and B.
- Motors for air fans should have variable speed, which help to maintain air pressure as per requirements, as there is difference in air pressure in working and non-working conditions.
- Air flow velocity of 0.36 m/sec to 0.56 m/sec is recommended as standard in laminar air flow ways.
- Routine Cleaning: Aseptic areas must undergo regular cleaning to maintain sterility. This includes wiping surfaces with disinfectants, cleaning filters, and using UV sterilization to kill any microorganisms that may have entered. Disinfection Protocols: The surfaces and equipment in the aseptic area must be disinfected using appropriate disinfectants, such as alcohol or hydrogen peroxide, before each use.